Ground-penetrating radar
 Ground-penetrating radar
Hardware
Ground-penetrating radar
Hardware
• MALA RAMAC/GPR Control Unit II (CU II)
• 25, 50, 100, 200 MHz Unshielded Antennas
• 250, 500 MHz Shielded Antennas
• Panasonic Toughbooks CF-18 and CF-29 for data acquisition and analysis
Software
• RAMAC Ground Vision for data acquisition
• REFLEXW for data analysis
Methodological principle
Ground-penetrating radar is a technique that uses high-frequency electromagnetic waves to acquire information on subsurface composition. The electromagnetic pulse is emitted from a transmitter antenna and propagates through the subsurface at a velocity determined by the dielectric properties of the subsurface materials. The pulse is reflected by inhomogeneities and layer boundaries and is received by a second antenna after a measured travel time (Schrott and Sass, 2008, Geomorphology).
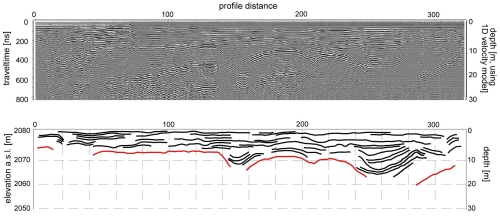
DC resistivity
 DC resistivity
Hardware
DC resistivity
Hardware
• GeoTomMK1E100 RES/IP/SP
• 110 Electrodes
• up to 400m profile length with 4m electrode spacing
• Panasonic Toughbooks CF-18 and CF-29 for data acquisition and analysis
Software
• GeoTom 7.x for data acquisition
• RES2DINV, RES3DINV, DC2DInvRes and BERT for data analysis
Methodological principle
Ground-penetrating radar is a technique that uses high-frequency electromagnetic waves to acquire information on subsurface composition. The electromagnetic pulse is emitted from a transmitter antenna and propagates through the subsurface at a velocity determined by the dielectric properties of the subsurface materials. The pulse is reflected by inhomogeneities and layer boundaries and is received by a second antenna after a measured travel time (Schrott and Sass, 2008, Geomorphology).
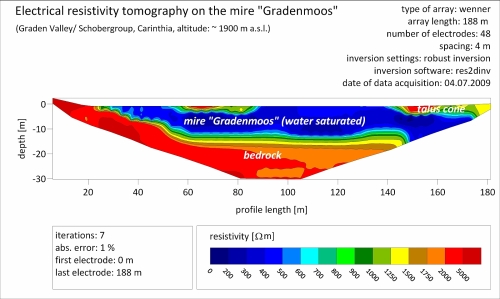
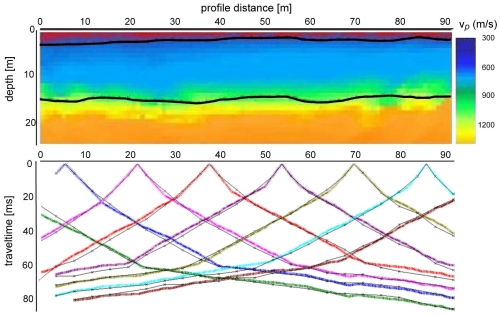
Refraction seismic
 Refraction seismic
Hardware
Refraction seismic
Hardware
• Geometrics Geode 24 channel seismograph
• 24 geophones with 14 Hz
• 48 geophones with 10 Hz
• 6 Cables with take outs of 5 – 10 m
• Panasonic Toughbook CF-29 and CF 18 for data acquisition and analysis
Software
• Seismodul control for data acquisition
• REFLEXW for data analysis
Methodological principle
The principle of seismic refraction is based on elastic waves travelling through different subsurface materials, such as sand, gravel, and bedrock, at different velocities. The denser the material, the faster the waves travel. On the basis of measured apparent velocities conclusions about subsurface structures can be drawn (Schrott and Sass, 2008, Geomorphology).
 Ground-penetrating radar
Hardware
• MALA RAMAC/GPR Control Unit II (CU II)
• 25, 50, 100, 200 MHz Unshielded Antennas
• 250, 500 MHz Shielded Antennas
• Panasonic Toughbooks CF-18 and CF-29 for data acquisition and analysis
Software
• RAMAC Ground Vision for data acquisition
• REFLEXW for data analysis
Methodological principle
Ground-penetrating radar is a technique that uses high-frequency electromagnetic waves to acquire information on subsurface composition. The electromagnetic pulse is emitted from a transmitter antenna and propagates through the subsurface at a velocity determined by the dielectric properties of the subsurface materials. The pulse is reflected by inhomogeneities and layer boundaries and is received by a second antenna after a measured travel time (Schrott and Sass, 2008, Geomorphology).
Ground-penetrating radar
Hardware
• MALA RAMAC/GPR Control Unit II (CU II)
• 25, 50, 100, 200 MHz Unshielded Antennas
• 250, 500 MHz Shielded Antennas
• Panasonic Toughbooks CF-18 and CF-29 for data acquisition and analysis
Software
• RAMAC Ground Vision for data acquisition
• REFLEXW for data analysis
Methodological principle
Ground-penetrating radar is a technique that uses high-frequency electromagnetic waves to acquire information on subsurface composition. The electromagnetic pulse is emitted from a transmitter antenna and propagates through the subsurface at a velocity determined by the dielectric properties of the subsurface materials. The pulse is reflected by inhomogeneities and layer boundaries and is received by a second antenna after a measured travel time (Schrott and Sass, 2008, Geomorphology).

 DC resistivity
Hardware
• GeoTomMK1E100 RES/IP/SP
• 110 Electrodes
• up to 400m profile length with 4m electrode spacing
• Panasonic Toughbooks CF-18 and CF-29 for data acquisition and analysis
Software
• GeoTom 7.x for data acquisition
• RES2DINV, RES3DINV, DC2DInvRes and BERT for data analysis
Methodological principle
Ground-penetrating radar is a technique that uses high-frequency electromagnetic waves to acquire information on subsurface composition. The electromagnetic pulse is emitted from a transmitter antenna and propagates through the subsurface at a velocity determined by the dielectric properties of the subsurface materials. The pulse is reflected by inhomogeneities and layer boundaries and is received by a second antenna after a measured travel time (Schrott and Sass, 2008, Geomorphology).
DC resistivity
Hardware
• GeoTomMK1E100 RES/IP/SP
• 110 Electrodes
• up to 400m profile length with 4m electrode spacing
• Panasonic Toughbooks CF-18 and CF-29 for data acquisition and analysis
Software
• GeoTom 7.x for data acquisition
• RES2DINV, RES3DINV, DC2DInvRes and BERT for data analysis
Methodological principle
Ground-penetrating radar is a technique that uses high-frequency electromagnetic waves to acquire information on subsurface composition. The electromagnetic pulse is emitted from a transmitter antenna and propagates through the subsurface at a velocity determined by the dielectric properties of the subsurface materials. The pulse is reflected by inhomogeneities and layer boundaries and is received by a second antenna after a measured travel time (Schrott and Sass, 2008, Geomorphology).

 Refraction seismic
Hardware
• Geometrics Geode 24 channel seismograph
• 24 geophones with 14 Hz
• 48 geophones with 10 Hz
• 6 Cables with take outs of 5 – 10 m
• Panasonic Toughbook CF-29 and CF 18 for data acquisition and analysis
Software
• Seismodul control for data acquisition
• REFLEXW for data analysis
Methodological principle
The principle of seismic refraction is based on elastic waves travelling through different subsurface materials, such as sand, gravel, and bedrock, at different velocities. The denser the material, the faster the waves travel. On the basis of measured apparent velocities conclusions about subsurface structures can be drawn (Schrott and Sass, 2008, Geomorphology).
Refraction seismic
Hardware
• Geometrics Geode 24 channel seismograph
• 24 geophones with 14 Hz
• 48 geophones with 10 Hz
• 6 Cables with take outs of 5 – 10 m
• Panasonic Toughbook CF-29 and CF 18 for data acquisition and analysis
Software
• Seismodul control for data acquisition
• REFLEXW for data analysis
Methodological principle
The principle of seismic refraction is based on elastic waves travelling through different subsurface materials, such as sand, gravel, and bedrock, at different velocities. The denser the material, the faster the waves travel. On the basis of measured apparent velocities conclusions about subsurface structures can be drawn (Schrott and Sass, 2008, Geomorphology).






